Posted on
Apr 28, 2025
Through Innovative Research
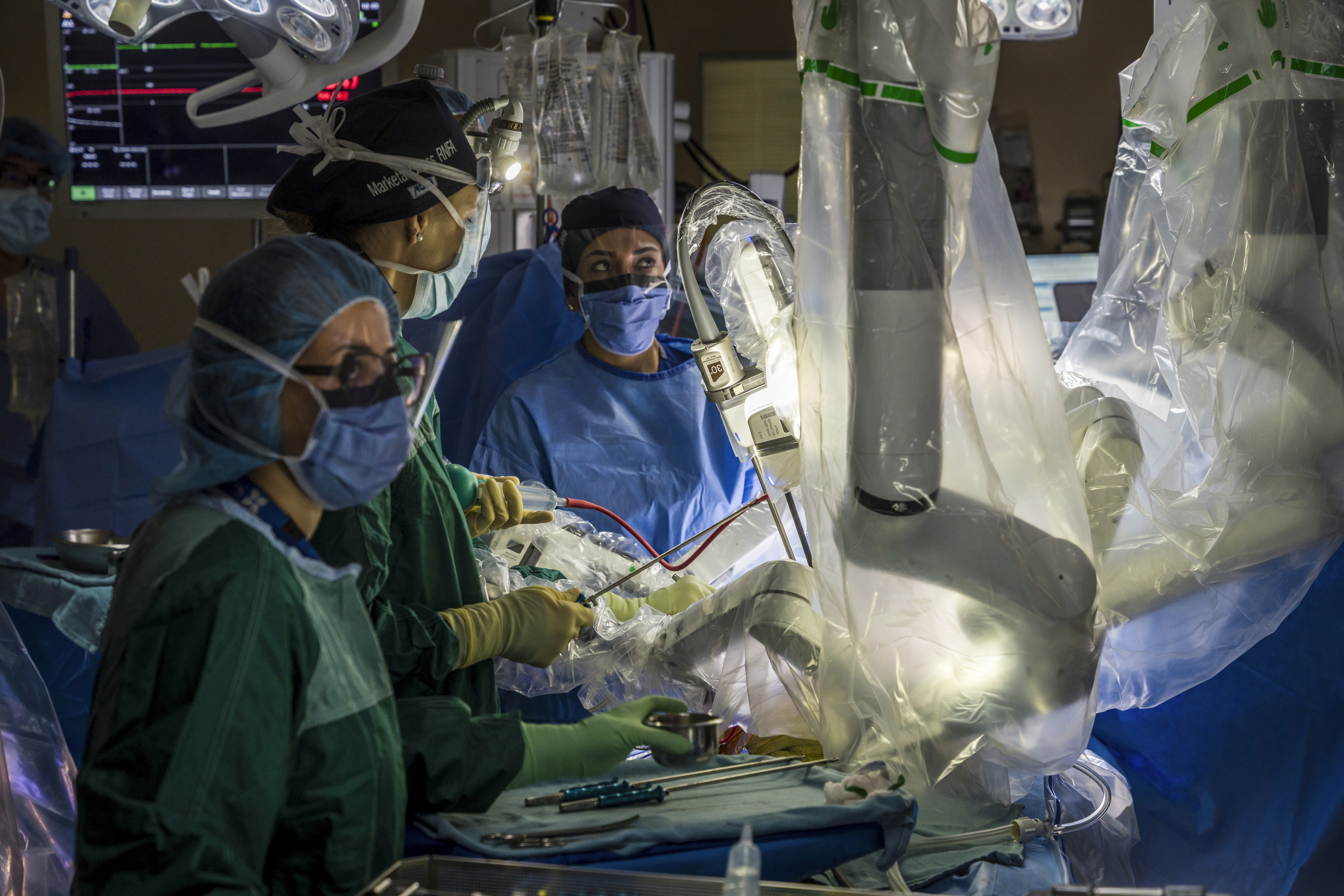
ROBOTIC MITRAL VALVE SURGERY: FROM PIONEERING STEPS TO MASTERING THE FUTURE
Over the past 25 years, robotic-assisted mitral valve surgery has shifted from a novel experiment to an established surgical option in cardiac care. The driving goal has been clear: to minimize patient trauma while maintaining or improving surgical outcomes. With smaller incisions, reduced recovery times, and enhanced operative precision, this technique has redefined how surgeons approach mitral valve repair.
The earliest attempts at minimally invasive mitral valve surgery in the late 1990s relied on limited instrumentation and 2D visualization. These approaches, while groundbreaking, faced barriers in dexterity and access. The arrival of the da Vinci Surgical System changed the field entirely. Three-dimensional magnified views, wristed instruments with seven degrees of freedom, and motion scaling gave surgeons unmatched precision inside the heart. This allowed for complex leaflet resections, chordal repairs, and annuloplasty to be performed through small thoracic ports instead of full sternotomy.
WHAT MADE IT POSSIBLE:
Modern robotic mitral valve surgery benefits from several transformative innovations:
High-Definition 3D Endoscopy – Immersive visualization of cardiac structures.
Wristed Robotic Instruments – Greater freedom of movement for delicate suturing.
Minimally Invasive Port Placement – Reduced trauma, pain, and scarring.
Improved Perfusion Techniques – Safer peripheral cannulation and endoaortic clamping.
Valve-Specific Tools – Custom annuloplasty devices and retractors for robotic use.
BENEFITS AND IMPACTS:
Robotic-assisted mitral valve surgery offers outcomes that benefit both patients and healthcare systems:
Lower postoperative pain and faster mobilization.
Reduced blood loss and fewer transfusion needs.
Shorter hospital stays and ICU times.
Comparable or superior long-term valve repair durability.
Better cosmetic results, which can improve patient satisfaction.
The future promises even more refined robotic platforms with haptic feedback, smaller instruments, and improved integration with imaging technologies. Artificial intelligence could eventually guide surgical planning and enhance intraoperative decision-making. However, accessibility and cost remain challenges to widespread adoption. Robotic-assisted mitral valve surgery represents more than a technological milestone. It reflects a shift in surgical philosophy toward maximizing precision while minimizing patient trauma. For patients, this means shorter recovery times, less postoperative pain, and improved quality of life; for surgeons, it offers tools that make complex repairs more reproducible and efficient. As the technology continues to mature, the boundaries of what is surgically possible will expand. With proper investment in training, infrastructure, and equitable access, roboticassisted mitral valve surgery could become the global standard for mitral repair; a future where complex heart surgery is performed through minimal incisions, with outcomes that were once unimaginable